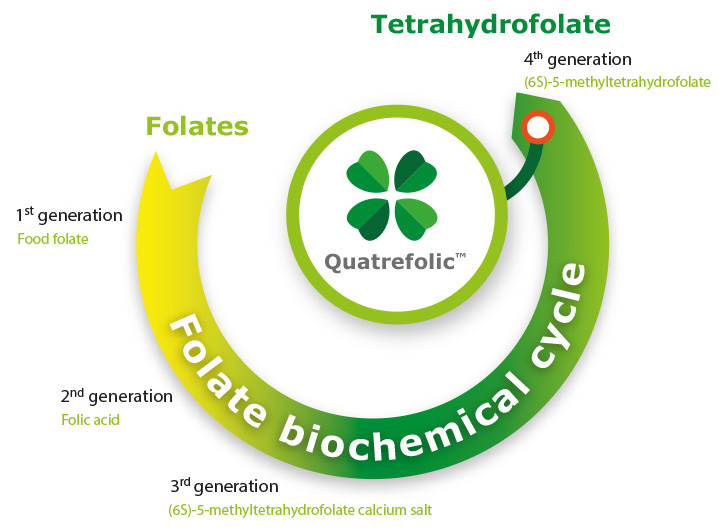
THE 4TH GENERATION FOLATE
Quatrefolic® is the fourth generation folate derivatives, a new generation of folate derivative made up of (6S)-5-methyltetra-hydrofolate and glucosamine salt which is able to overcome the existing calcium salt form limitations related to stability, poor solubility and bioavailability. This new source of folate has four key critical factors that make it a successful product: bioavailability, safety, stability and formulation flexibility.
Actually there are differences in the forms:
1st generation – Food folate
2nd generation – Folic acid
Folic acid lacks coenzyme activity and must be reduced to the metabolically active form within the cell, through a series of biochemical steps before it can be used by the body’s cells in vital metabolic pathways such as DNA production, cell reproduction and homocysteine metabolism.
3rd generation – (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolate calcium salt
The calcium salt of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate is available commercially and represents the third generation of folate. Until now, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate calcium salt was the only folic acid derivative available on the market, and able to penetrate the body cells without the need of further metabolism process.
The 4th generation: Quatrefolic®
Quatrefolic® represents the fourth generation folate endowed with long lasting stability as well as a peculiarly high water solubility, improved bioavailability and well established safety.
Solubility
QUATREFOLIC® is 100 times more soluble in water than calcium salt. Quatrefolic® demonstrates a surprisingly high solubility in water greater than 1 g/ml – compared with the slight solubility of the reference compound, (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolate calcium salt (1.1 g/100 ml).
Bioavailability
The pre-clinical study was a direct bioavailability comparison between Quatrefolic®, the (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolic calcium salt and folic acid. After single oral dosing in rats, Quatrefolic® showed plasma levels about 20% higher than those reached after a corresponding dose of the calcium salt.
Stability
Quatrefolic® shows an extraordinary long lasting chemical stability guaranteeing a quite unaltered purity even after several months, and an assay reduction in 18 months less than 1%, allowing easy handling and storage.
Safety
Quatrefolic®, as glucosamine salt of (6S)-5-methyltetrahydrofolate has been the subject of an extensive and relevant number of biological and toxicological studies in order to prove the safety and tolerability of this revolutionary folate.